Correct answer is option B
As decreases, increases and hence the speed of photo electron increases. The chances of photo electron to meet the anode increases and hence photo electric current increases.
56. (AIEEE 2006 )
The anode voltage of a photocell is kept fixed. The wavelength of the light falling on the cathode is gradually changed. The plate current of the photocell varies as follows
(A) 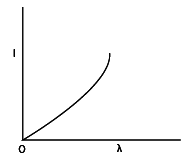
(B) 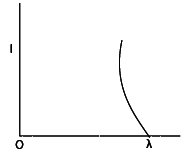
(C) 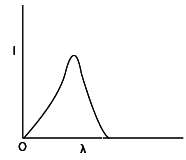
(D) 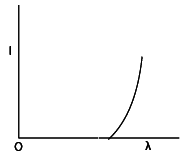
Correct answer is option B
As decreases, increases and hence the speed of photo electron increases. The chances of photo electron to meet the anode increases and hence photo electric current increases.
57. (AIEEE 2004 )
The work function of a substance is 4.0eV The longest wavelength of light that can cause photo-electron emission from this substance is approximately.
(A) 310nm
(B) 400nm
(C) 540nm
(D) 220nm
Correct answer is A
For the longest
wavelength to
emit photo
electron
58. (AIEEE 2004 )
According to Einstein's photoelectric equation, the plot of the kinetic energy of the emitted photo electrons from a metal Vs the frequency, of the incident radiation gives as straight the whose slope
(A) depends both on the intensity of the radiation and the metal used
(B) depends on the intensity of the radiation
(C) depends on the nature of the metal used
(D) is the same for the all metals and independent of the intensity of the radiation
Correct answer is D
Einstein's photoelectric equation is given by
where is the maximum kinetic energy of the emitted photoelectrons, is Planck's constant, is the frequency of the incident radiation, and is the work function of the metal (the minimum energy needed to eject an electron).
If you plot against , you will get a straight line with slope (Planck's constant) and y-intercept (the negative of the work function). The slope of the line (which is ) does not depend on the intensity of the radiation or the type of metal used. Instead, it is a universal constant.
Therefore, the correct answer is:
Option D: The slope is the same for all metals and independent of the intensity of the radiation.
59. (AIEEE 2003 )
Two identical photo-cathodes receive light of frequencies and . If the velocities of the photo electrons (of mass ) coming out are respectively and then
(A)
(B)
(C)
(D)
Correct answer is option A
For one photo cathode
For another
photo cathode
Subtracting
from
we get
60. (AIEEE 2002 )
Sodium and copper have work functions 2.3eV and 4.5eV respectively. Then the ratio of the wavelengths is nearest to
(A) 1 : 2
(B) 4 : 1
(C) 2 : 1
(D) 1 : 4
Correct answer is C
We know that
work
function is
the energy
required and
energy
as
for light